Protective Cultivation Techniques: Enhancing Crop Production and Quality
Protective cultivation techniques are transformative strategies in modern agriculture designed to improve crop production and quality by shielding plants from adverse environmental conditions. With climate variability and extreme weather becoming increasingly common, these techniques offer farmers and growers innovative solutions to ensure stable and high-yielding crops. This article explores various protective cultivation techniques, their benefits, and their impact on enhancing crop production and quality.
1. Introduction to Protective Cultivation Techniques
What is Protective Cultivation?
Protective cultivation involves using physical structures or controlled environments to safeguard crops from harmful external factors such as extreme temperatures, excessive rainfall, and strong winds. These techniques aim to create optimal growing conditions that enhance plant growth and yield.
Importance in Modern Agriculture
- Mitigating Climate Risks: Protective techniques help manage risks associated with climate change and unpredictable weather patterns.
- Boosting Productivity: By creating favorable growing conditions, these techniques can lead to increased crop yields and improved quality.
2. Common Protective Cultivation Techniques
Greenhouses
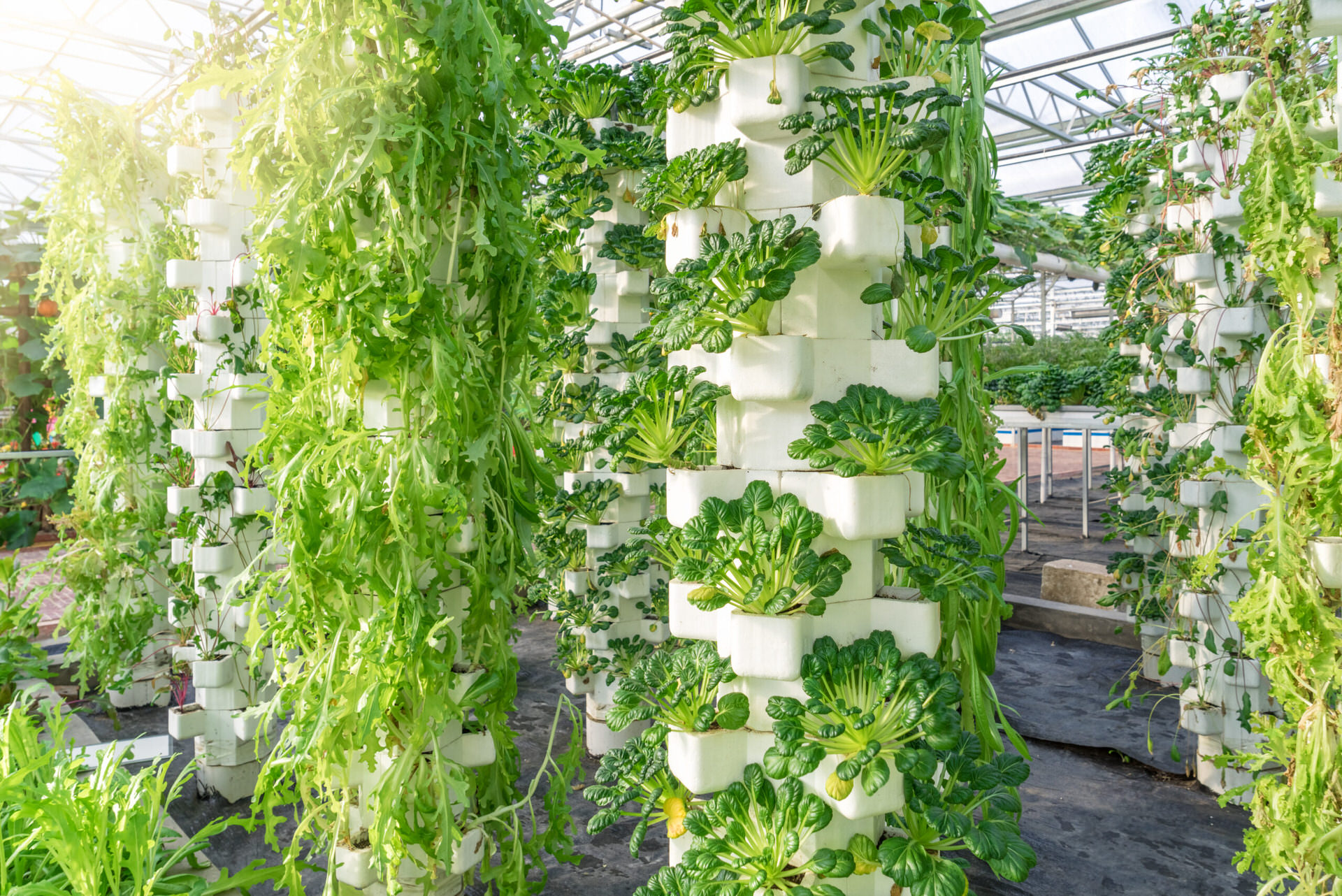
Greenhouses are enclosed structures that provide a controlled environment for plants. They offer protection from harsh weather, pests, and diseases while allowing precise control over temperature, humidity, and light.
- Types of Greenhouses:
- Glasshouses: Traditional greenhouses made from glass that provide excellent light transmission.
- Polycarbonate Greenhouses: Durable structures with double-walled panels that offer better insulation and UV protection.
- High-Tech Climate-Controlled Greenhouses: Equipped with advanced systems for temperature, humidity, and CO2 control.
Polytunnels
Polytunnels, or hoop houses, are semi-permanent structures covered with plastic sheeting. They provide protection from rain, wind, and cold temperatures while allowing good light transmission.
- Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: More affordable than greenhouses.
- Versatile: Suitable for a wide range of crops and easy to install.
- Limitations: Less durable and may require more frequent maintenance.
Row Covers
Row covers are lightweight fabrics placed over rows of plants to protect them from frost, pests, and wind. They can be used in combination with other protective methods for added security.
- Types:
- Floating Row Covers: Provide frost protection and can be used for early planting.
- Netting: Shields plants from insect pests.
- Shade Cloth: Reduces heat stress and sunburn in hot climates.
Cold Frames
Cold frames are low, enclosed structures that trap heat from the sun to create a warmer microclimate for plants. They are commonly used for starting seeds or extending the growing season.
- Design: Typically has a hinged lid or transparent cover to allow sunlight in and provide ventilation.
- Applications: Useful for early spring planting and overwintering hardy crops.
Shade Structures
Shade structures are designed to protect plants from intense sunlight and heat. They help prevent sunburn and reduce water loss through evaporation.
- Materials: Shade cloths, netting, and mesh.
- Benefits: Essential in hot climates to reduce heat stress and improve plant health.
3. Benefits of Protective Cultivation Techniques
Enhanced Crop Yields
Protective cultivation techniques create a stable growing environment, which helps maximize crop yields by reducing stress and promoting healthy plant development.
Improved Crop Quality
By shielding plants from environmental stressors, protective techniques result in higher-quality produce with fewer defects, blemishes, and diseases.
Extended Growing Seasons
These techniques allow for earlier planting and later harvesting, extending the growing season and enabling multiple crop cycles per year.
Resource Efficiency
Protective cultivation methods often lead to more efficient use of water, nutrients, and energy, as they mitigate the impact of external factors on resource use.
Risk Reduction
By minimizing exposure to extreme weather conditions and pests, protective techniques reduce the risks associated with crop failure and ensure more reliable production.
4. Challenges and Considerations
Cost
Initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs for protective structures can be significant. However, the long-term benefits often justify the expense.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is required to ensure the effectiveness and longevity of protective systems, including repairs, cleaning, and adjustments.
Climate Adaptability
Choosing the appropriate protective technique depends on the specific climate and environmental conditions of the growing area. Some techniques may be better suited to certain climates or crop types.
Knowledge and Expertise
Successful implementation of protective cultivation techniques requires understanding crop needs, environmental management, and system operation.
5. Future Trends in Protective Cultivation
Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology are enhancing protective cultivation techniques. Innovations include smart greenhouses with automated climate control systems, advanced materials for improved insulation, and integrated pest management systems.
Sustainability Focus
Future developments in protective cultivation will likely emphasize sustainability, including energy-efficient systems, renewable energy sources, and sustainable materials.
Integration with Precision Agriculture
Protective cultivation techniques are increasingly being integrated with precision agriculture practices, using data-driven approaches to optimize growing conditions and resource use.
Conclusion
Protective cultivation techniques play a crucial role in modern agriculture by enhancing crop production and quality in the face of unpredictable climates and extreme weather. By employing methods such as greenhouses, polytunnels, row covers, cold frames, and shade structures, farmers can create optimal growing conditions, improve yields, and ensure high-quality produce. Despite the challenges and costs associated with these techniques, their benefits in risk management and resource efficiency make them invaluable tools for achieving sustainable and resilient agriculture. As technology advances and sustainability becomes a greater focus, protective cultivation will continue to evolve, offering even more effective solutions for farmers around the world.