Telehealth Revolution: Enhancing Healthcare Access in Connecticut
Introduction: Telehealth has emerged as a game-changer in the healthcare landscape of Connecticut, offering innovative solutions to bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers. In this article, we’ll explore the dynamic world of telehealth in Connecticut, examining its benefits, applications, challenges, and the future it holds for healthcare delivery.
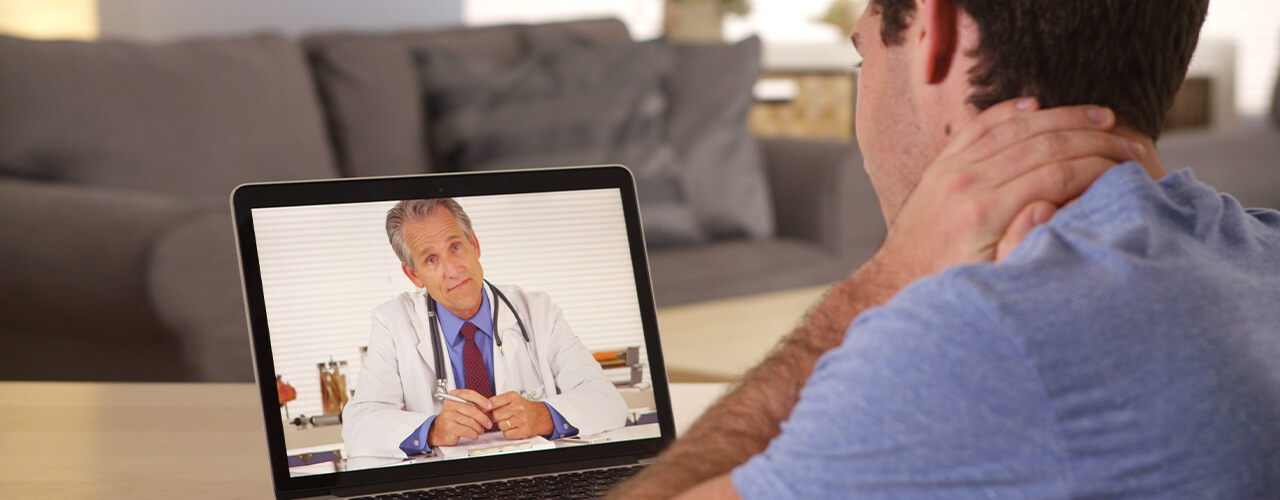
Understanding Telehealth: Telehealth, a cutting-edge approach to healthcare delivery, utilizes technology to facilitate remote consultations, diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of patients. Through video conferencing, secure messaging, and other digital platforms, telehealth brings healthcare services directly to patients’ fingertips, eliminating geographical barriers and enhancing accessibility.
The Rise of Telehealth in Connecticut: In recent years, telehealth has experienced exponential growth in Connecticut, fueled by advancements in technology, changing patient preferences, and the need for innovative healthcare solutions. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of telehealth, highlighting its importance in ensuring continuity of care and minimizing disruptions to healthcare services.
Benefits of Telehealth in Connecticut: Telehealth offers a multitude of benefits for both patients and healthcare providers in Connecticut:
Enhanced Accessibility: Telehealth enables individuals living in rural or underserved areas to access healthcare services without the need for extensive travel or time off work. Convenience and Flexibility: Patients can schedule appointments, receive medical advice, and access follow-up care from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for in-person visits and minimizing wait times. Cost Savings: Telehealth consultations are often more cost-effective than traditional in-person visits, leading to savings in terms of transportation expenses, childcare costs, and missed workdays. Improved Patient Outcomes: Telehealth facilitates proactive management of chronic conditions, timely intervention for acute illnesses, and regular monitoring of patients’ health status, leading to better health outcomes and reduced hospital admissions. Safety and Infection Control: Telehealth minimizes the risk of exposure to infectious diseases, such as COVID-19, by limiting in-person contact and reducing the need for patients to visit crowded healthcare facilities. Applications of Telehealth in Connecticut: Telehealth has a wide range of applications across various healthcare specialties and settings in Connecticut:
Primary Care: Telehealth enables primary care providers to conduct virtual consultations, address non-urgent medical concerns, and manage chronic conditions through remote monitoring and follow-up. Specialty Care: Telehealth extends access to specialized medical services, including mental health counseling, dermatology consultations, and cardiology assessments, allowing patients to receive timely care without lengthy wait times. Urgent Care: Telehealth platforms offer on-demand medical advice and treatment for minor injuries, common illnesses, and urgent medical concerns, reducing the burden on emergency departments and urgent care centers. Chronic Disease Management: Telehealth supports the remote management of chronic conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma, through virtual check-ins, medication adjustments, and lifestyle coaching. Preventive Care: Telehealth facilitates preventive care services, such as annual wellness visits, immunizations, and health screenings, promoting early detection of health issues and proactive management of risk factors. Challenges and Considerations: While telehealth offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges and considerations in Connecticut:
Digital Divide: Disparities in internet access, digital literacy, and access to technology may limit the adoption of telehealth among underserved populations, exacerbating existing healthcare inequities. Reimbursement Policies: Uncertainty surrounding reimbursement policies and coverage for telehealth services may impact healthcare providers’ willingness to offer telehealth options and patients’ ability to afford care. Privacy and Security: Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data transmitted through telehealth platforms is paramount to maintaining patient trust and compliance with healthcare regulations. Regulatory and Licensure Issues: State licensure requirements, credentialing processes, and regulatory frameworks may vary for healthcare providers practicing telehealth across state lines, posing logistical challenges for telehealth implementation. Future Outlook: Despite these challenges, the future of telehealth in Connecticut appears promising, with continued advancements in technology, evolving regulatory frameworks, and growing acceptance among patients and healthcare providers. As telehealth becomes more integrated into the healthcare ecosystem, it has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery, improve patient outcomes, and enhance access to care for all residents of Connecticut.
Conclusion: Telehealth has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare delivery, offering unparalleled convenience, accessibility, and flexibility for patients and providers in Connecticut. By embracing telehealth solutions, healthcare stakeholders can overcome challenges, expand access to care, and create a more resilient and patient-centered healthcare system. As telehealth continues to evolve and innovate, it promises to shape the future of healthcare delivery in Connecticut and beyond.