Understanding ADHD Therapy: Approaches to Manage Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
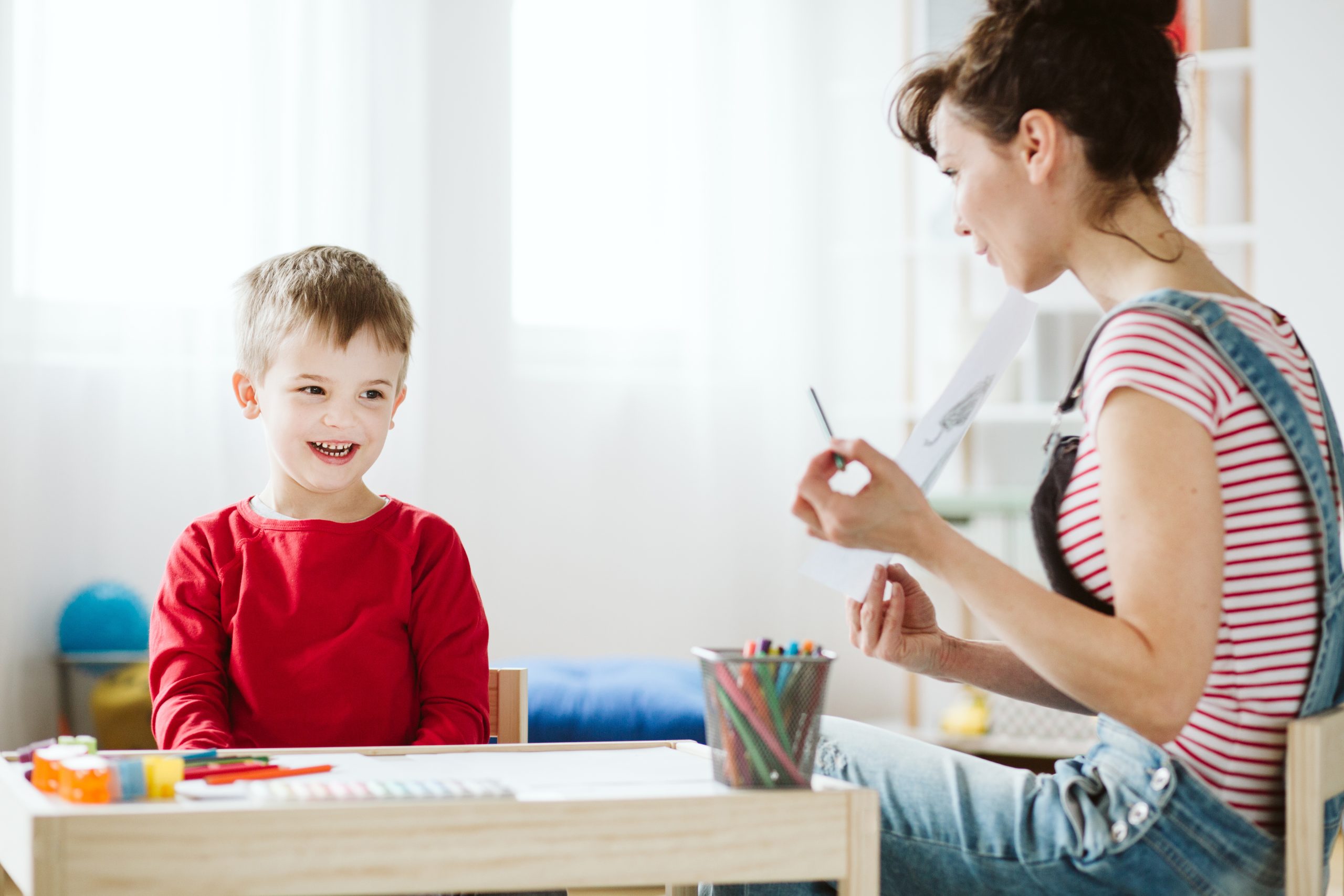
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Managing ADHD often requires a multifaceted approach, with therapy playing a crucial role in helping individuals develop coping strategies and improve their quality of life. This article will explore the various types of ADHD therapy, their benefits, and how to find the right support.
What is ADHD?
ADHD is a chronic condition that can significantly impact various aspects of life, including academic performance, relationships, and work productivity. The symptoms of ADHD can be categorized into two primary types:
- Inattentive Type: Difficulty sustaining attention, following through on tasks, and organizing activities.
- Hyperactive-Impulsive Type: Excessive fidgeting, interrupting others, and difficulty waiting for one’s turn.
Many individuals exhibit symptoms from both categories, leading to the combined type of ADHD. The causes of ADHD are not fully understood but are believed to involve genetic, environmental, and neurological factors.
Importance of ADHD Therapy
Therapy is essential for managing ADHD, as it provides individuals with the tools and strategies they need to navigate daily challenges. While medication can effectively alleviate some symptoms, therapy addresses the emotional, behavioral, and social aspects of the disorder.
Benefits of ADHD Therapy
- Improved Coping Strategies: Therapy helps individuals develop effective coping mechanisms to manage symptoms and reduce frustration.
- Enhanced Self-Esteem: Supportive therapeutic environments foster self-awareness and self-acceptance, helping individuals build confidence.
- Better Relationships: Therapy can improve communication skills and interpersonal relationships by addressing behavioral challenges associated with ADHD.
- Goal Setting and Time Management: Therapists can help individuals create structured plans, improving organization and task completion.
- Parental Support: Therapy provides parents with strategies to support their children with ADHD, promoting a better home environment.
Types of ADHD Therapy
Several therapeutic approaches are effective in managing ADHD. Each type of therapy can be tailored to meet the individual’s unique needs and circumstances.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is one of the most commonly used therapeutic approaches for ADHD. CBT focuses on identifying negative thought patterns and replacing them with more constructive ones. This therapy can help individuals with ADHD:
- Recognize and change unhelpful beliefs about themselves and their abilities.
- Develop practical skills to manage time, organize tasks, and prioritize responsibilities.
- Learn coping strategies to deal with emotional challenges, such as frustration and anxiety.
2. Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy is centered on modifying specific behaviors associated with ADHD. This approach involves:
- Reinforcement Strategies: Providing rewards for positive behaviors and consequences for negative behaviors to encourage desired changes.
- Parent Training: Educating parents about effective behavior management techniques that they can use at home to support their children.
3. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals with ADHD improve focus and reduce impulsivity. These techniques encourage individuals to be present in the moment, enhancing self-regulation and emotional control.
4. Psychoeducation
Psychoeducation involves educating individuals and their families about ADHD, its symptoms, and its effects. This understanding helps reduce stigma, promotes self-advocacy, and fosters a supportive environment for individuals with ADHD.
5. Social Skills Training
For individuals with ADHD who struggle with social interactions, social skills training can be beneficial. This therapy focuses on improving communication, understanding social cues, and developing healthy relationships. Role-playing and group therapy can be effective methods within this approach.
6. Family Therapy
Family therapy addresses the dynamics within the family unit and how they relate to ADHD symptoms. This therapy aims to improve communication, reduce conflict, and promote understanding among family members. It can be particularly helpful for families with children diagnosed with ADHD.
7. Coaching and Organizational Skills Training
Coaching focuses on helping individuals with ADHD set goals, develop plans, and improve time management and organizational skills. Coaches work with clients to create structured routines and identify strategies that work best for their unique needs.
How to Find the Right ADHD Therapy
Finding the right therapist or treatment approach is crucial for effective ADHD management. Here are some steps to guide the process:
1. Seek Professional Guidance
Start by consulting with a healthcare provider, such as a pediatrician, psychiatrist, or psychologist, who specializes in ADHD. They can provide referrals to qualified therapists experienced in treating ADHD.
2. Consider Credentials
Look for therapists who have specific training and experience in treating ADHD. Credentials may include Licensed Clinical Social Worker (LCSW), Licensed Professional Counselor (LPC), or psychologist with expertise in ADHD.
3. Evaluate Treatment Approaches
Discuss potential therapy options with the therapist to understand their approach and how it aligns with your or your child’s needs.
4. Check for Insurance Coverage
Inquire about insurance coverage for therapy sessions. Many insurance plans cover mental health services, but it’s essential to verify which providers are in-network.
5. Trial Sessions
Consider scheduling initial sessions with a few therapists to determine the best fit. A positive therapeutic relationship is crucial for effective treatment.
Conclusion: Embracing ADHD Therapy for a Better Quality of Life
ADHD therapy plays a vital role in helping individuals manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. By utilizing various therapeutic approaches tailored to individual needs, therapy can enhance emotional regulation, improve relationships, and foster a greater understanding of ADHD.
Whether you or a loved one is navigating the challenges of ADHD, seeking professional help is a proactive step toward emotional well-being. With the right support, individuals with ADHD can thrive in their personal and professional lives, transforming their challenges into strengths.